Vaccination
Vaccination: Protecting Lives, One Shot at a Time
Vaccination is one of the greatest breakthroughs in medical science. It has saved millions of lives, eradicated deadly diseases, and continues to protect people of all ages from illnesses that once caused mass suffering and death. Despite its proven success, misinformation still clouds the minds of many—making education on this life-saving practice more critical than ever.
What Is Vaccination?
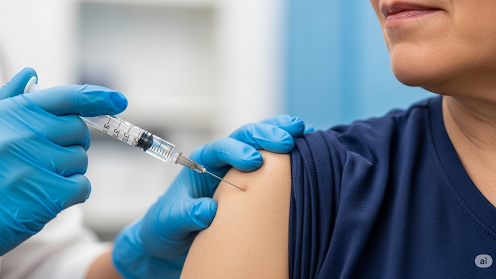
Vaccination is the process of stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight off harmful pathogens such as viruses or bacteria. It involves introducing a harmless part or weakened form of the disease-causing germ (antigen) into the body, usually through an injection, which then “trains” the immune system to recognize and fight the real disease if it ever appears.
This safe exposure prepares the body to defend itself, often for life, without causing illness.
Why Vaccination Is Necessary
Before vaccines, outbreaks of diseases like measles, polio, diphtheria, and smallpox killed or disabled millions. Today, because of widespread vaccination:
Smallpox has been eradicated worldwide.
Polio is nearly extinct, with only a few cases remaining globally.
Measles, mumps, rubella, tetanus, hepatitis, HPV, and many more diseases are preventable.
Vaccination is not just about individual protection—it creates herd immunity, shielding those who cannot be vaccinated, such as newborns or those with compromised immune systems.
What Does Vaccination Prevent?
Vaccines protect against numerous deadly or disabling diseases, including:
Childhood diseases like measles, polio, whooping cough, and mumps
Liver diseases like hepatitis A and B
Cervical and other cancers caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV)
Flu and COVID-19, which can cause severe illness and death
Tetanus, which is life-threatening and cannot be spread from person to person
Without vaccination, even once-controlled diseases can re-emerge, as seen in recent measles outbreaks in under-vaccinated communities.
Common Reactions and Misconceptions
Vaccines are overwhelmingly safe. Some people may experience mild side effects like low-grade fever, swelling at the injection site, or tiredness—signs the immune system is responding as it should.
There is no credible evidence linking vaccines to conditions like autism. Rigorous testing and global health reviews have consistently proven vaccines to be safe and effective.
How to Ensure Proper Vaccination
Follow national immunization schedules—these are carefully planned based on age, health, and disease risk.
Keep vaccination records up to date for your children and yourself.
Consult your healthcare provider if you have medical conditions or are pregnant.
Stay informed about booster shots, especially for diseases like COVID-19 or tetanus.
Vaccination is a shared responsibility—it protects not just you, but your family, community, and future generations.
Summary
Vaccination is a powerful medical tool that trains the body’s immune system to recognize and fight harmful viruses or bacteria without causing illness. By introducing a harmless part of the germ into the body, vaccines help build immunity and prevent future infections. Vaccination has played a key role in eradicating or controlling deadly diseases like smallpox, polio, measles, hepatitis, and COVID-19. It not only protects individuals but also contributes to herd immunity, safeguarding entire communities. Though some people may experience mild side effects such as fever or swelling, vaccines are overwhelmingly safe and effective. Following national immunization schedules, keeping records updated, and staying informed about boosters are essential steps in ensuring protection. Choosing vaccination is a life-saving decision that benefits both personal and public health.
Final Thoughts
Vaccination is not just a medical procedure—it’s a powerful act of prevention. It stops deadly diseases before they start, saves healthcare costs, and promotes longer, healthier lives. In a world filled with preventable threats, vaccines are one of humanity’s strongest defenses.
By choosing vaccination, you’re not only protecting yourself—you’re protecting everyone around you. Stay informed. Stay protected. Get vaccinated.